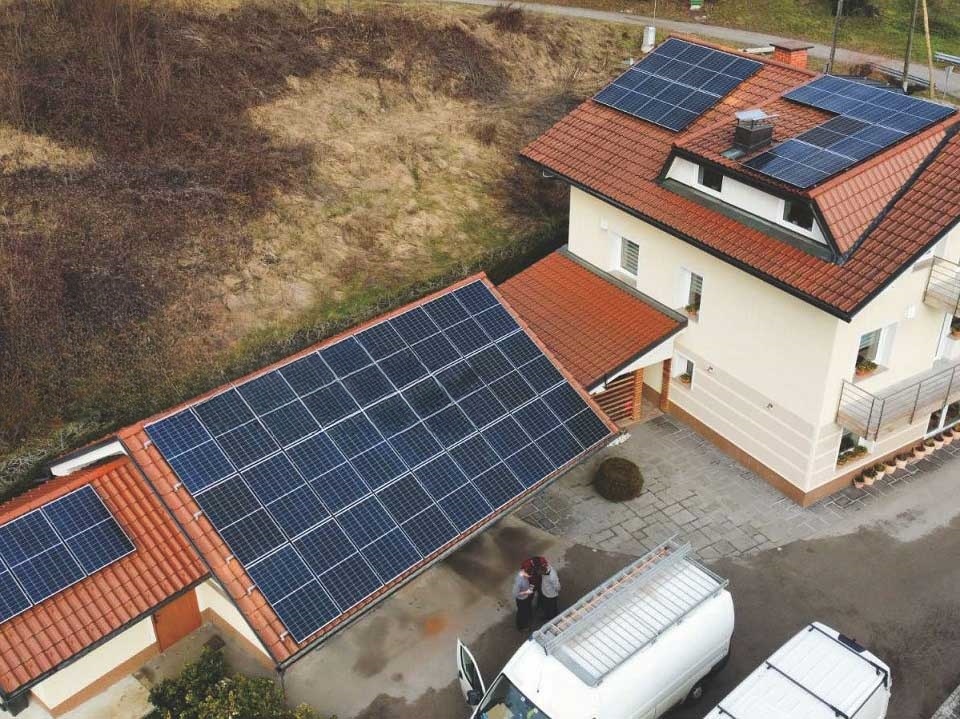
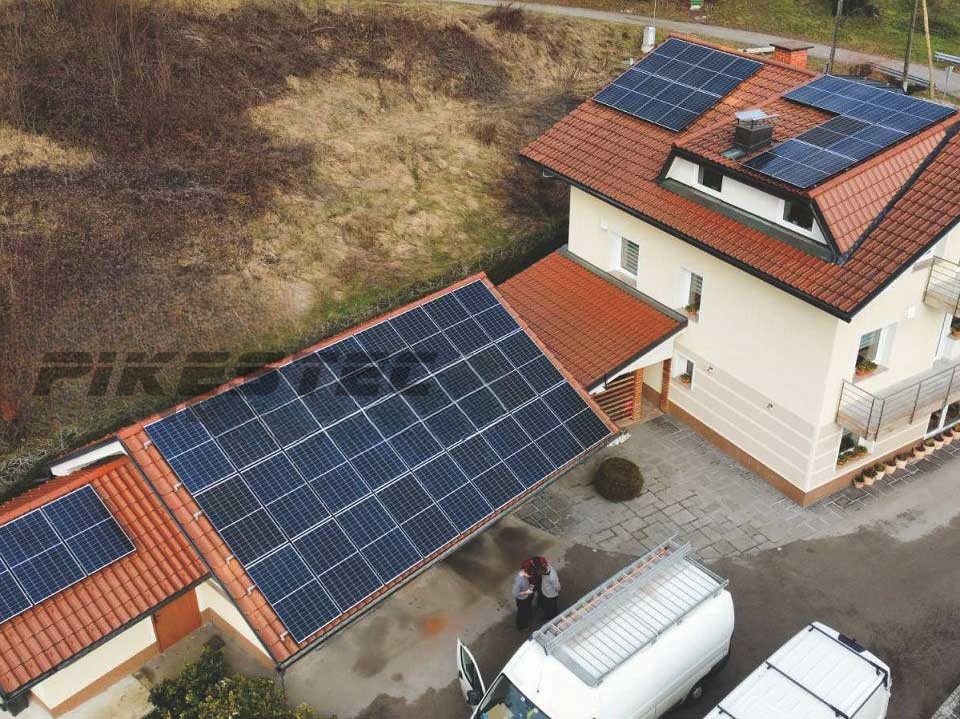
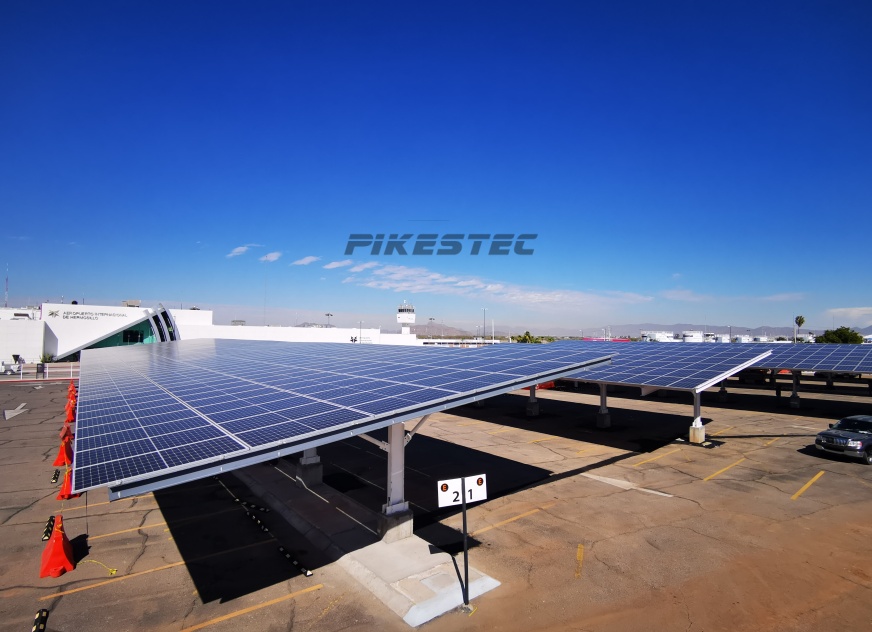
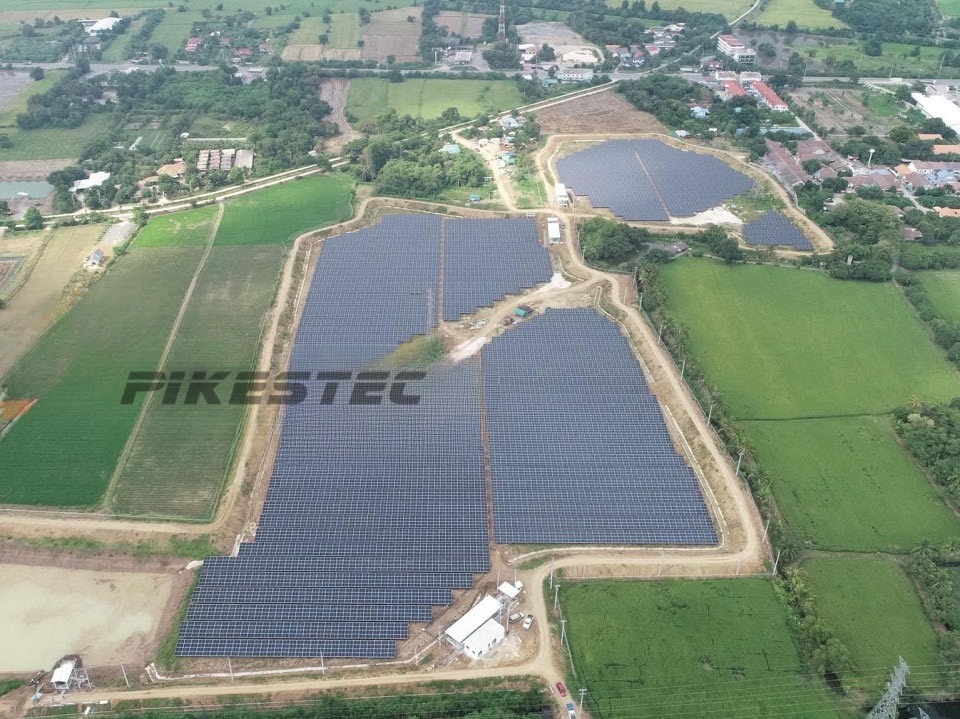
Solar Penal Cell Product Characteristics:
It appears there might be a typo in your request. Assuming you meant “solar panel cell,” here are the expanded product characteristics for a solar panel cell that is suitable for the distribution market, embodies a modern style, offers the highest efficiency, and comes with a better product warranty and service:
A solar cell or photovoltaic cell (PV cell) is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect.It is a form of photoelectric cell, a device whose electrical characteristics (such as current, voltage, or resistance) vary when it is exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices are often the electrical building blocks of photovoltaic modules, known colloquially as “solar panels“. Almost all commercial PV cells consist of crystalline silicon, with a market share of 95%. Cadmium telluride thin-film solar cells account for the remainder.The common single-junction silicon solar cell can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage of approximately 0.5 to 0.6 volts.
Photovoltaic cells may operate under sunlight or artificial light. In addition to producing energy, they can be used as a photodetector (for example infrared detectors), detecting light or other electromagnetic radiation near the visible range, or measuring light intensity.
The operation of a PV cell requires three basic attributes:
The absorption of light, generating excitons (bound electron-hole pairs), unbound electron-hole pairs (via excitons), or plasmons.
The separation of charge carriers of opposite types.
The separate extraction of those carriers to an external circuit.
In contrast, a solar thermal collector supplies heat by absorbing sunlight, for the purpose of either direct heating or indirect electrical power generation from heat. A “photoelectrolytic cell” (photoelectrochemical cell), on the other hand, refers either to a type of photovoltaic cell (like that developed by Edmond Becquerel and modern dye-sensitized solar cells), or to a device that splits water directly into hydrogen and oxygen using only solar illumination.
Photovoltaic cells and solar collectors are the two means of producing solar power
Better Product Warranty and Service
After-sales service:
- 15-year Warranty for Materials and Processing
- 25-year Warranty for Extra Linear Power Output
applications
Application of solar cells as an alternative energy source for vehicular applications is a growing industry. Electric vehicles that operate off of solar energy and/or sunlight are commonly referred to as solar cars.These vehicles use solar panels to convert absorbed light into electrical energy that is then stored in batteries.There are multiple input factors that affect the output power of solar cells such as temperature, material properties, weather conditions, solar irradiance and more.
The first instance of photovoltaic cells within vehicular applications was around midway through the second half of the 1900’s. In an effort to increase publicity and awareness in solar powered transportation Hans Tholstrup decided to set up the first edition of the World Solar Challenge in 1987.It was a 3000 km race across the Australian outback where competitors from industry research groups and top universities around the globe were invited to compete. General Motors ended up winning the event by a significant margin with their Sunraycer vehicle that achieved speeds of over 40 mph.Contrary to popular belief however solar powered cars are one of the oldest alternative energy vehicles.
Current solar vehicles harness energy from the Sun via Solar panels which are a collected group of solar cells working in tandem towards a common goal.These solid-state devices use quantum mechanical transitions in order to convert a given amount of solar power into electrical power.The electricity produced as a result is then stored in the vehicle’s battery in order to run the motor of the vehicle.Batteries in solar-powered vehicles differ from those in standard ICE cars because they are fashioned in a way to impart more power towards the electrical components of the vehicle for a longer duration.