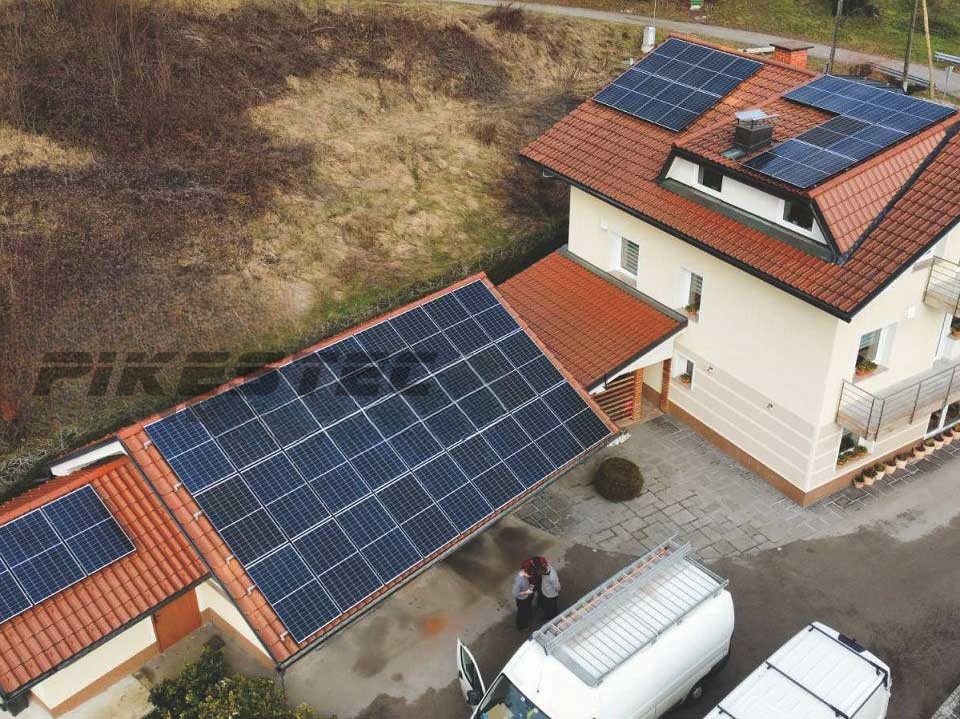
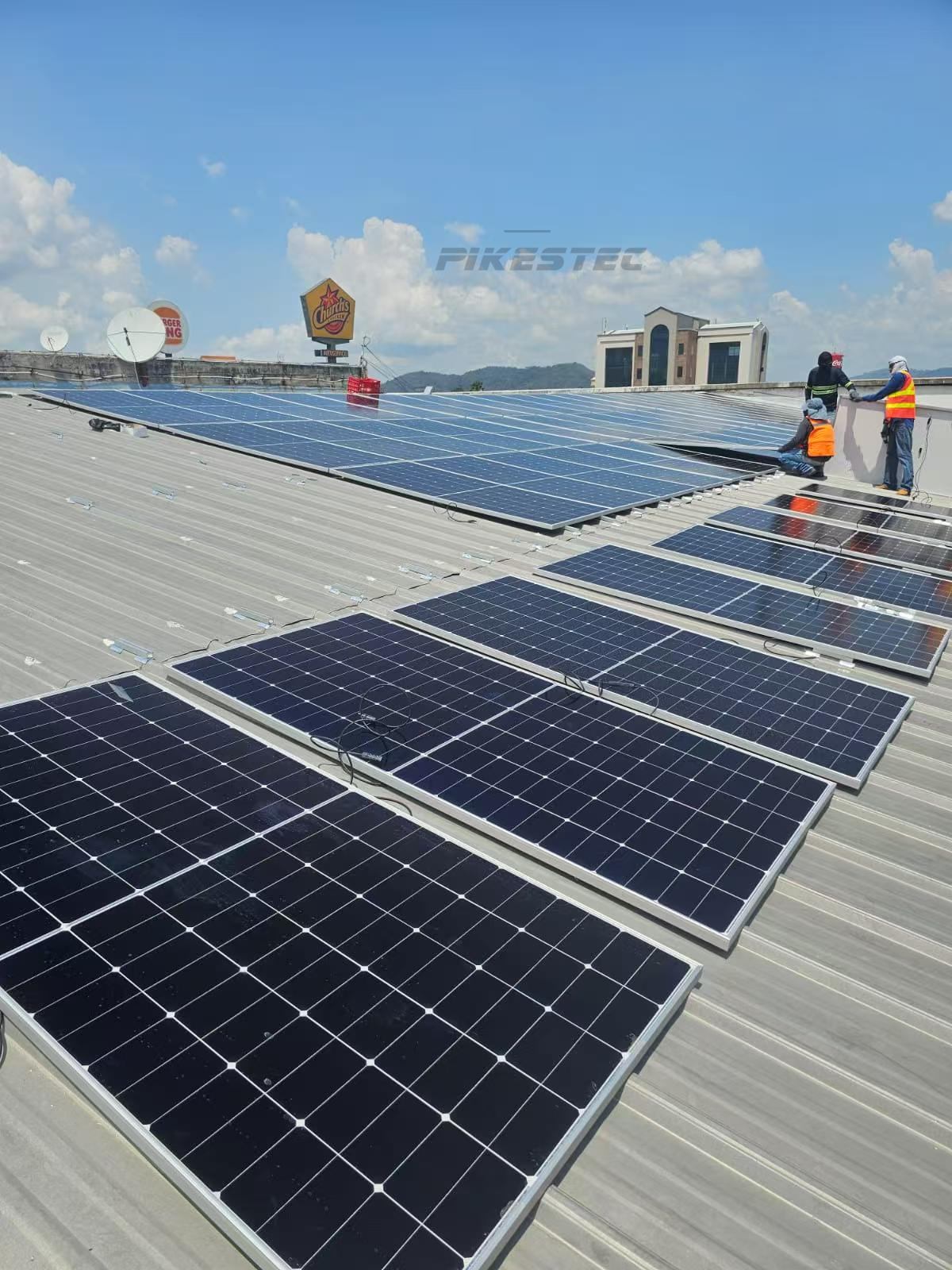
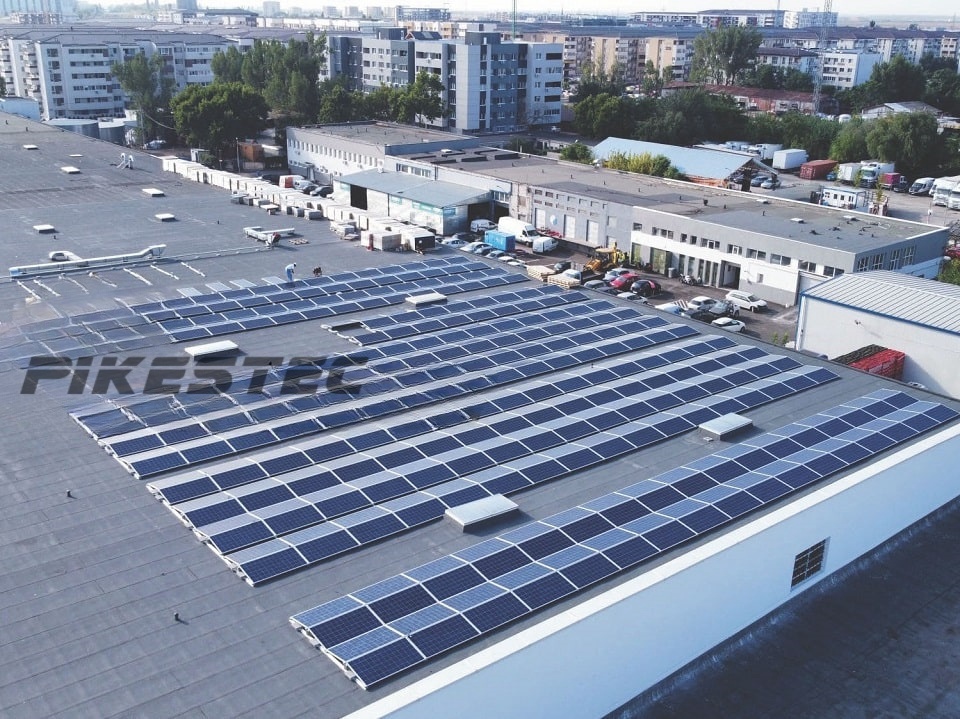
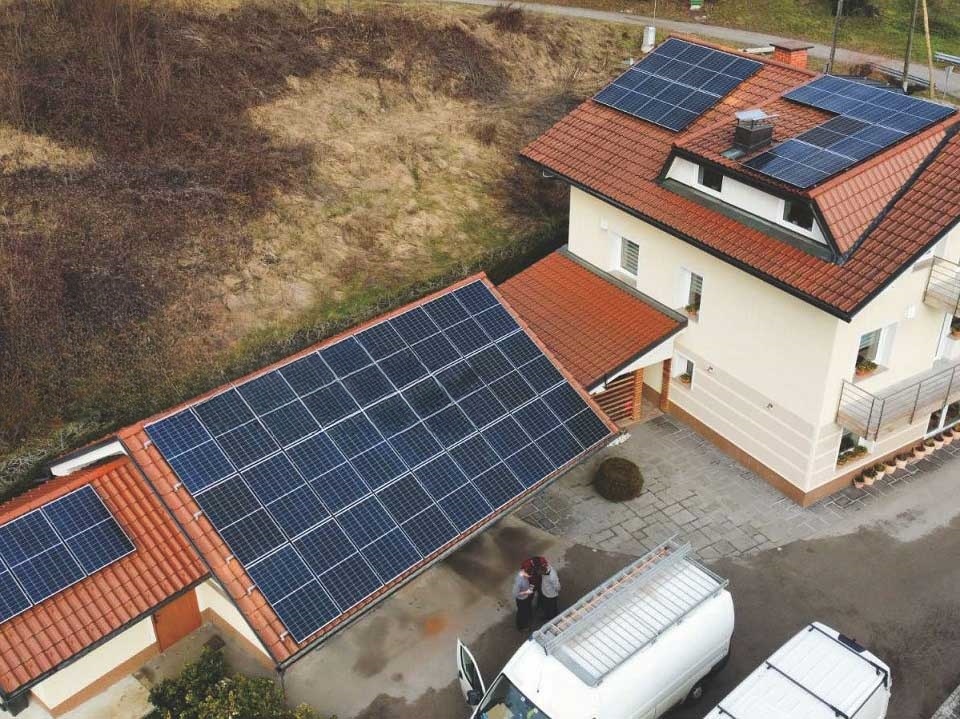
N-TYPE TOPCON TECHNOLOGY PV MODULES
Photovoltaic modules, commonly known as solar panels, are devices that convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. They are made up of multiple solar cells, which are typically made from silicon-based materials. When sunlight strikes these cells, it excites electrons, generating an electric current.
Key components of photovoltaic modules include:
- Solar Cells: These are the basic units that convert sunlight into electricity. They are usually made from crystalline silicon, though thin-film technologies using materials like cadmium telluride or amorphous silicon are also used.
- Encapsulation: Solar cells are encapsulated in materials such as ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and surrounded by a transparent cover (often tempered glass) to protect them from the elements while allowing sunlight to pass through.
- Frame: Most solar panels have a metal frame around the edges to provide structural support and protect the edges of the module.
- Backsheet: This is a layer on the back of the module that protects the cells from moisture and mechanical damage.
Photovoltaic modules come in various sizes and power ratings, typically ranging from about 100 watts to several hundred watts per module. They are interconnected to form solar arrays that can generate electricity for residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications.
The efficiency of photovoltaic modules has been steadily improving over the years, driven by advancements in materials, manufacturing processes, and research into new technologies. These modules play a crucial role in renewable energy systems by providing clean, sustainable electricity without emissions or fuel consumption.


Photovoltaic Modules
A PV module consists of many PV cells wired in parallel to increase current and in series to produce a higher voltage. 36 cell modules are the industry standard for large power production.
The module is encapsulated with tempered glass (or some other transparent material) on the front surface, and with a protective and waterproof material on the back surface. The edges are sealed for weatherproofing, and there is often an aluminum frame holding everything together in a mountable unit. In the back of the module there is a junction box, or wire leads, providing electrical connections.
There are currently four commercial production technologies for PV Modules:
Single Crystalline
The statement you provided seems to refer to an older production technique for solar modules, possibly monocrystalline silicon, which was once considered the most efficient but also the most expensive method. However, the efficiency range of 10% to 12% is relatively low for modern monocrystalline silicon solar modules. Today, monocrystalline silicon solar modules typically have efficiencies ranging from 15% to 20% or higher, and some high-efficiency models can reach efficiencies above 22%.
Polycrystalline or Multicrystalline
This has a slightly lower conversion efficiency compared to single crystalline but manufacturing costs are also lower. Module efficiency averages about 10% to 11%*
String Ribbon
This is a refinement of polycrystalline production, there is less work in production so costs are even lower. Module efficiency averages 7% to 8%*
Amorphous or Thin Film
Silicon material is vaporized and deposited on glass or stainless steel. The cost is lower than any other method. Module efficiency averages 5% to 7%*






